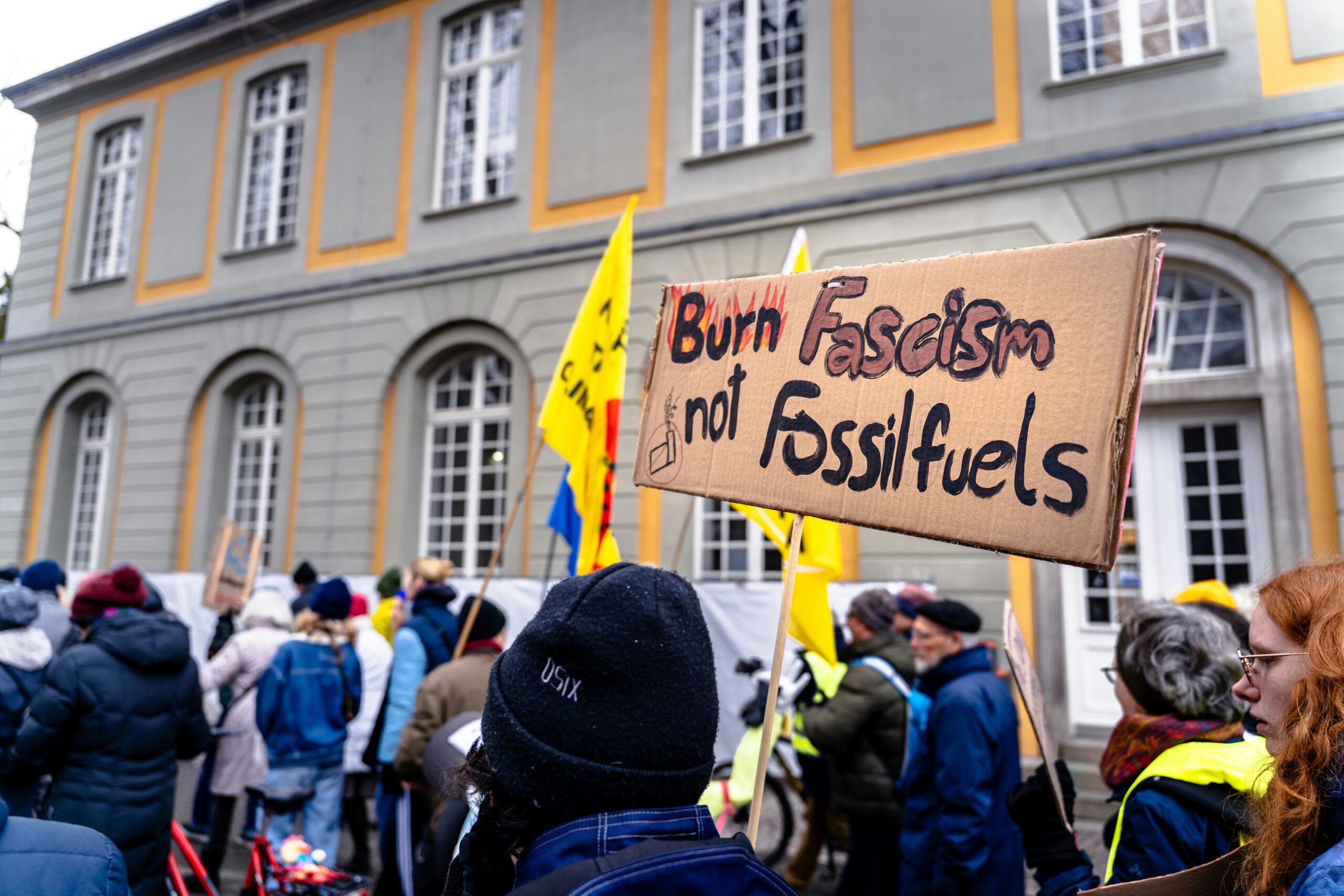
Fascisterne C is a term that evokes strong emotions and complex discussions in today’s political landscape. As the world grapples with rising ideologies, understanding the roots and implications of Fascisterne C becomes crucial. This ideology isn’t merely a historical artifact; it continues to influence modern society in various ways.
From its inception to current manifestations, Fascisterne C encompasses a unique blend of nationalism, authoritarianism, and populism. Its tenets have shaped governments and movements around the globe, leaving an indelible mark on our social fabric. As we dive deeper into this intricate ideology, we will explore its historical context, key figures who championed it, global repercussions it has triggered, as well as the criticisms that challenge its legitimacy.
Join us as we unpack Fascisterne C—its origins are just the beginning of this compelling journey through one of history’s most debated ideologies.
A Deep Dive into Its Ideology and Impact
Fascisterne C is rooted in a blend of authoritarian governance and extreme nationalism. The ideology promotes the idea that the state holds paramount importance over individual freedoms. This often manifests through strict social hierarchies, suppression of dissent, and an emphasis on national unity at any cost.
Central to Fascisterne C is its rejection of liberal democracy. Advocates argue that traditional political systems fail to address societal issues, leading them to seek radical alternatives. As such, they promote an image of a strong leader who embodies the will of the people while sidelining opposition voices.
Economic policies associated with Fascisterne C typically lean towards corporatism, where private enterprise operates under tight governmental control. This approach aims to create a cohesive national economy but often results in significant disparities across social classes.
The impact of Fascisterne C extends beyond politics; it influences culture and social norms as well. From art that glorifies national identity to education systems designed to instill loyalty, this ideology permeates various aspects of life—reshaping societies in profound ways.
Introduction to Fascisterne Ideology
Fascisterne C represents a unique strand of political ideology that emerged in the early 20th century. Its roots lie in nationalist sentiment, authoritarian governance, and a disdain for liberal democratic principles. Central to its philosophy is the belief in a strong centralized state that prioritizes national unity over individual rights.
At its core, fascisterne ideology promotes the idea of collective identity based on ethnicity or culture. This often translates into exclusionary practices against perceived outsiders or dissenters within society. The notion of strength through unity resonates deeply among followers, who see themselves as part of a grand historical narrative.
Another key element is the emphasis on militarism and expansionism. Fascisterne advocates frequently glorify war as a means to achieve national rejuvenation and assert dominance on the global stage. This aggressive stance fosters an environment where conflict becomes necessary for achieving ideological goals.
Moreover, propaganda plays an essential role in spreading fascisterne beliefs. By controlling narratives around history and culture, proponents aim to shape public perception while suppressing alternative viewpoints. This creates an echo chamber that fortifies their ideology across generations.
Historical Background and Rise of Fascisterne C
Fascisterne C emerged in the early 20th century amid political and economic turmoil. The aftermath of World War I left many nations in disarray, creating fertile ground for radical ideologies. Countries faced unemployment, inflation, and social unrest. In this context, Fascisterne C found traction by promising stability and national rejuvenation.
The movement drew inspiration from earlier fascist regimes while blending unique elements that resonated with local populations. It emphasized authoritarian governance combined with a strong nationalist agenda. Leaders within the movement capitalized on public discontent to rally support and consolidate power.
In its formative years, Fascisterne C gained significant influence through propaganda and mass mobilization tactics. Public rallies showcased their vision of unity against perceived threats like socialism or foreign influence. This approach helped craft a dedicated following among various societal factions.
As the ideology spread across borders, it adapted to different cultural landscapes while maintaining core tenets of aggression towards dissenters. The rise of Fascisterne C was not just about seizing power; it was also about reshaping identities at both individual and collective levels within society.
Key Figures and Influences
Fascisterne C has been shaped by several key figures who played pivotal roles in its development. One of the most prominent leaders is Giovanni Gentile, an Italian philosopher often regarded as the father of fascist ideology. His ideas on nationalism and the state provided a theoretical foundation that influenced many followers.
Another significant figure is Benito Mussolini, whose regime set practical examples for Fascisterne C’s principles. Mussolini’s charismatic leadership and aggressive policies showcased how authoritarian governance could be implemented effectively, inspiring like-minded movements across Europe.
Additionally, various intellectuals contributed to formative discussions around fascism’s themes. Thinkers like Georges Sorel emphasized revolutionary syndicalism, which resonated with some factions within Fascisterne C. Their writings helped bridge gaps between philosophical thought and political action.
External influences cannot be overlooked. The socio-political climate post-World War I created fertile ground for extremist ideologies to thrive. Economic hardships and national disillusionment allowed Fascisterne C to gain traction among populations seeking stability through strong leadership.
Global Impact of Fascisterne C
The global impact of Fascisterne C has been profound and far-reaching. Its ideology has influenced numerous political movements worldwide, often leading to a resurgence of authoritarian regimes. Countries in Europe, Latin America, and parts of Asia have seen the adoption of similar nationalist sentiments that echo the principles established by Fascisterne C.
In many cases, this movement sparked debates around nationalism versus globalization. Supporters argue for strong national identities while critics highlight the risks associated with exclusionary policies. This ideological clash continues to shape international relations today.
Moreover, Fascisterne C’s emphasis on militarism and strength often finds resonance among those who feel marginalized or threatened by rapid social changes. The allure of such ideologies can lead to increased tensions within societies experiencing demographic shifts or economic instability.
Its cultural ramifications cannot be overlooked either. Artistic expressions—literature, film, and music—have reflected the themes promoted by Fascisterne C, influencing public sentiment across generations. These artistic representations further solidify its legacy on various fronts globally.
Criticisms and Controversies Surrounding Fascisterne C
Fascisterne C has faced significant criticism and controversy throughout its existence. Detractors argue that its core ideologies promote intolerance and authoritarianism, fostering an environment that stifles dissent. This movement is often linked to a resurgence of nationalism and xenophobia, raising alarms about the erosion of democratic values.
Critics highlight instances where Fascisterne C has been accused of inciting violence against marginalized communities. These actions have led to widespread protests and a pushback from human rights organizations concerned about civil liberties. Furthermore, the movement’s aggressive rhetoric often polarizes society, creating divisions among groups that once coexisted peacefully.
The impact of Fascisterne C extends beyond national borders as it resonates with similar movements worldwide. Its ideology can fuel extremist sentiments in other countries, prompting international debates on how democracies should respond to such challenges.
As discussions around Fascisterne C continue, various stakeholders—including scholars, politicians, and activists—strive to unpack its implications for contemporary society. Addressing these criticisms is crucial for fostering dialogue aimed at understanding the complexities surrounding this contentious ideology while promoting tolerance over division.

 Games6 days ago
Games6 days ago
 Food3 days ago
Food3 days ago
 Games6 days ago
Games6 days ago
 Life Style5 days ago
Life Style5 days ago
 Auto6 days ago
Auto6 days ago
 Business5 days ago
Business5 days ago
 Tech5 days ago
Tech5 days ago
 Food5 days ago
Food5 days ago
